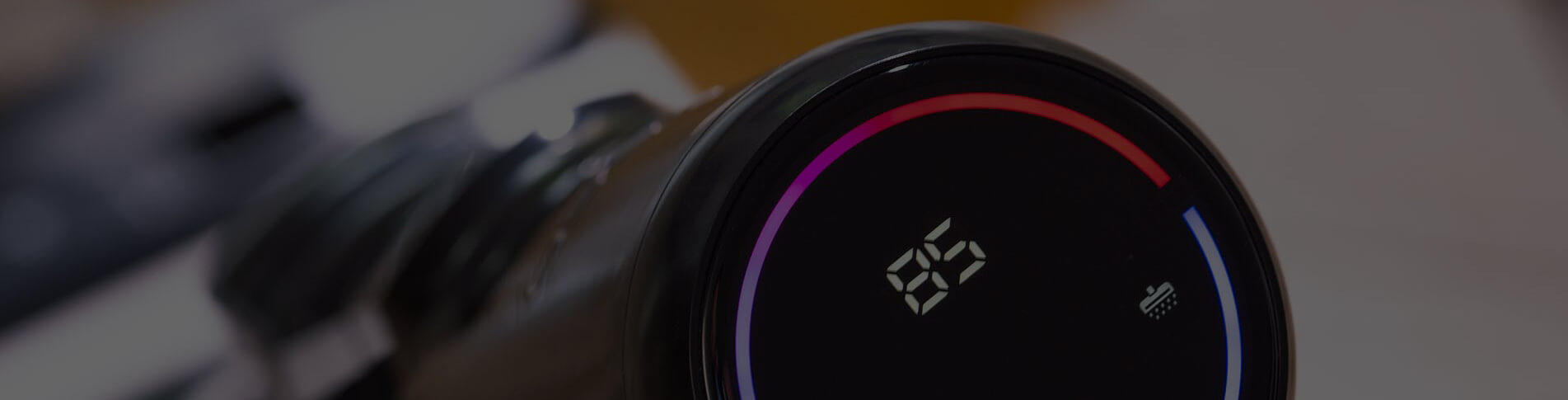
Las pantallas TFT y OLED tienen cada una sus propias ventajas únicas y escenarios aplicables, y es difícil generalizar cuál es "mejor".
1. Principios técnicos y estructura
Pantalla TFT: La pantalla TFT (Thin Film Transistor), también conocida como pantalla de cristal líquido con transistor de película delgada, es una tecnología de pantalla de cristal líquido en color de matriz activa. Utiliza transistores de película delgada para controlar el brillo de cada píxel y controla la conmutación de los píxeles cambiando la corriente para lograr la visualización de la imagen. Las pantallas TFT requieren una luz de fondo para iluminar la pantalla, y la luz de fondo normalmente utiliza LED o CCFL (lámparas fluorescentes de cátodo frío).
Pantalla OLED: La pantalla OLED (diodo emisor de luz orgánico), es decir, pantalla de diodo emisor de luz orgánico, es una tecnología de pantalla autoiluminada. Utiliza una capa muy fina de materiales orgánicos y un sustrato de vidrio (o un sustrato orgánico flexible) que emite luz cuando una corriente eléctrica lo atraviesa. Cada píxel de la pantalla OLED emite luz de forma independiente, sin necesidad de retroiluminación.
2. Efecto de visualización y rendimiento del color.
Pantalla TFT:
Reproducción de color: El pantalla TFT Funciona bien en la reproducción del color y puede presentar imágenes claras y naturales. Aunque su saturación de color puede ser ligeramente inferior a la de las pantallas OLED, en la mayoría de los escenarios de aplicación, el rendimiento del color de las pantallas TFT es suficiente para satisfacer las necesidades del usuario.
Contraste y rendimiento del negro: dado que las pantallas TFT requieren una luz de fondo para iluminar la pantalla, es posible que no puedan mostrar negros muy profundos. Sin embargo, con el continuo avance de la tecnología, algunas pantallas TFT de alta gama han podido lograr un buen rendimiento en este sentido.
Ángulo de visión: las pantallas TFT suelen tener un alto brillo y amplios ángulos de visión, lo que significa que los usuarios pueden obtener una buena experiencia visual en diferentes entornos de iluminación y ángulos de visión.
Pantalla OLED:
Colores brillantes y alto contraste: las pantallas OLED son autoluminosas, por lo que pueden lograr un mayor contraste y un rendimiento de colores más vivos. Su relación de contraste suele alcanzar más de 100.000:1, lo que puede mostrar negros muy profundos y colores vivos.
Amplio ángulo de visión: las pantallas OLED tienen ángulos de visión muy amplios, que a menudo alcanzan los 170 grados o más, lo que significa que el color y el contraste de la imagen no cambiarán significativamente cuando la pantalla se vea desde diferentes ángulos.
Rendimiento detallado: porque cada píxel del pantalla OLED Emite luz de forma independiente, puede presentar más detalles y capas, haciendo la imagen más delicada y realista.
3. Consumo de energía y vida útil
Pantalla TFT:
Consumo de energía: aunque las pantallas TFT requieren un módulo de retroiluminación para iluminar la pantalla, su consumo total de energía sigue siendo relativamente bajo (en comparación con tecnologías anteriores). Sin embargo, en comparación con las pantallas OLED, las pantallas TFT pueden consumir más energía cuando muestran contenido de alto brillo.
Vida útil: La vida útil de una pantalla TFT es relativamente larga porque está compuesta de materiales inorgánicos y tiene una mayor durabilidad. En condiciones de uso normal, la vida útil de una pantalla TFT puede alcanzar décadas.
Pantalla OLED:
Bajo consumo de energía: las pantallas OLED no requieren un módulo de retroiluminación, por lo que casi no consumen energía cuando muestran contenido negro u oscuro. Esto permite que las pantallas OLED logren un menor consumo de energía al mostrar imágenes y videos dinámicos. Sin embargo, cuando se muestra contenido blanco o de alto brillo, el consumo de energía de las pantallas OLED puede aumentar.
Vida útil relativamente corta: las pantallas OLED están compuestas de materiales orgánicos y se ven fácilmente afectadas por factores ambientales como la oxidación y la humedad, lo que reduce su vida útil. La vida útil de una pantalla OLED puede oscilar entre unos pocos miles y decenas de miles de horas. Además, mostrar la misma imagen durante mucho tiempo también puede provocar "quema de pantalla".
4. Precio y áreas de aplicación
Pantalla TFT:
Precio: Dado que la tecnología de pantalla TFT es madura y ampliamente utilizada, su costo de producción es relativamente bajo, por lo que el precio también es relativamente barato. Esto hace que las pantallas TFT se utilicen ampliamente en muchos campos.
Campos de aplicación: las pantallas TFT se utilizan principalmente en monitores de computadora, televisores de pantalla plana, teléfonos inteligentes, tabletas y otros campos. Debido a sus ventajas de colores brillantes, alta definición y velocidad de respuesta rápida, las pantallas TFT se utilizan ampliamente en productos electrónicos de pantalla grande.
Pantalla OLED:
Precio: El costo de producción de las pantallas OLED es relativamente alto, por lo que el precio también es relativamente caro. Sin embargo, a medida que la tecnología continúa avanzando y la producción aumenta, el precio de las pantallas OLED va disminuyendo gradualmente.
Campos de aplicación: las pantallas OLED se utilizan principalmente en productos electrónicos de alta gama, como teléfonos inteligentes, televisores, monitores, etc. Debido a sus ventajas como autoiluminación, ultradelgada, alto contraste y amplio ángulo de visión, las pantallas OLED tienen mejor rendimiento al mostrar imágenes dinámicas y pantallas de juegos. Además, las pantallas OLED también se utilizan ampliamente en dispositivos de pantalla curva y plegable, lo que brinda más posibilidades para el diseño de dispositivos.
5. Sugerencias completas de comparación y selección.
En resumen, las pantallas TFT y las pantallas OLED tienen cada una sus propias ventajas y escenarios aplicables. Al elegir, los usuarios deben tener en cuenta sus necesidades reales y su presupuesto. Aquí hay algunas sugerencias:
Si busca un rendimiento de alto costo y un rendimiento de color estable, y tiene mayores requisitos de vida útil y durabilidad de la pantalla, entonces las pantallas TFT pueden ser una mejor opción.
Si tiene requisitos más altos en cuanto a delgadez, ligereza, velocidad de respuesta y contraste de la pantalla, y no le importa pagar un precio más alto, entonces la pantalla OLED es una buena opción. Especialmente para los usuarios que necesitan mirar pantallas durante largos períodos de tiempo, las pantallas OLED pueden brindar una experiencia visual más cómoda y realista.
En resumen, al elegir la tecnología de pantalla, los usuarios deben considerar de manera integral factores como sus necesidades, presupuesto y rendimiento del producto para tomar la decisión que mejor se adapte a sus necesidades.








 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية


 IPv6 RED SOPORTADA
IPv6 RED SOPORTADA
